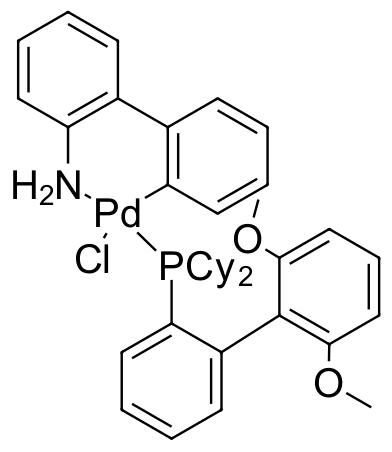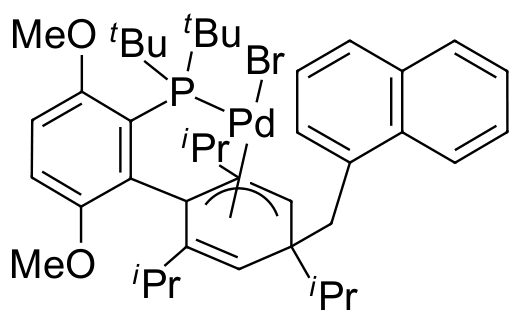Buchwald CX Precatalysts
Enabling Advanced Pd-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Chemistry
The pursuit of novel synthetic methodologies in organometallic chemistry continues to drive innovation in catalyst design and application. Umicore's broad portfolio of Buchwald precatalysts reflects a paradigm shift in palladium-mediated cross-coupling chemistry and offers researchers unprecedented control over bond formation processes.
Engineered for precision: Highly active palladium precatalysts and tunable biarylphosphine ligands for advanced cross-coupling.
The Buchwald research program has systematically developed a wide-ranging library of highly active palladium precatalysts and complementary biarylphosphine ligands specifically engineered for cross-coupling applications. The ligand framework generally features electron-rich biarylphosphines with highly tunable steric and electronic properties. The corresponding Buchwald precatalysts exhibit remarkable stability under ambient conditions, demonstrating resistance to air, moisture, and elevated temperatures while maintaining excellent solubility in standard organic solvents. Critically, these systems enable quantitative generation of the active L-Pd(0) species under mildly basic conditions without requiring external reducing agents, providing precise stoichiometric control over the ligand-to-palladium ratio and facilitating cross-coupling transformations at significantly decreased catalyst loadings and reduced reaction times.
From lab to scale: G2 and G3 technologies optimized for industrial cross-coupling.
Umicore's second and third-generation Buchwald catalyst technologies have been made available on industrial scale for advanced commercial cross-coupling applications. The second-generation (G2) precatalysts represent a significant structural advancement over their predecessors, replacing the phenethylamine backbone of first-generation (G1) complexes with a biphenyl-based ligand framework. This architectural modification enables the generation of the active Pd(0) species at ambient temperature using mild phosphate or carbonate bases, dramatically expanding the operational window for these catalysts. The third-generation (G3) addresses limitations inherent to G1 and G2 precatalysts through strategic ligand modification. Replacement of the chloride anion in G2 precatalysts with a more electron-withdrawing, non-coordinating methanesulfonate anion yields the third-generation (G3) precatalysts, which accommodate exceptionally bulky ligands (ex: CX401). Additionally, these precatalysts demonstrate remarkable solution stability, maintaining activity over extended periods.
Next-gen performance: Enhanced ligand frameworks and anion exchange for broader reactivity and solution stability.
Both G2 and G3 catalyst families demonstrate exceptional efficacy across diverse coupling applications, including Suzuki–Miyaura reactions, Negishi cross-couplings, Buchwald-Hartwig aminations, Sonagashira couplings, a-arylations, aminocarbonylations, and cyanations, establishing broad utility in synthetic organic chemistry. The ligands, precatalysts, and associated methodologies developed within the Buchwald research program and applied by the broader scientific community continue to demonstrate their utility for challenging transformations.
Catalyst control redefined: Enabling challenging transformations with reduced loadings and mild conditions.
The Umicore Buchwald CX catalyst portfolio offers researchers access to highly efficient, stable, and versatile catalyst systems. Through systematic structural advances in the different generations, these precatalysts enable unprecedented control over diverse bond-forming processes while operating under mild conditions with reduced catalyst loadings. The continued application of this catalyst platform promises to enable challenging organic chemistry and industrial process development.
Buchwald palladacycles involving a Buchwald ligand:
Umicore CX121 - Pd(SPhos)G2
CAS Number: 1375325-64-6
Empirical Formula: Pd(SPhos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)]Cl
CX121, also known as Pd(SPhos)G2, is a second-generation SPhos precatalyst. It has demonstrated higher yields, higher turnover rates, and reduced protodeboronation compared with catalysts formed in situ with either Pd(OAc)2 or Pd2dba3. It has primarily found application as a precatalyst for C-C bond-forming reactions.
Umicore CX122 - Pd(XPhos)G2
CAS Number: 1310584-14-5
Empirical formula: Pd(XPhos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)]Cl
The palladium-based catalyst CX122, also known as Pd(XPhos)G2, is a notable precatalyst in organic synthesis, particularly for carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bond formations. Similar to CX121, it is recognized for its superior performance derived from its ability to rapidly activate.
CX123, also known as Pd(RuPhos)G2, has been shown to be an effective catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling and Buchwald-Hartwig aminations under demanding conditions.
Examples of C-C bond forming reactions where CX123 has been most effective:
- Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of (hetero)aryl bromides and (hetero)aryl boronic acids or esters
- polythiophenes by Negishi catalyst transfer polymerization
CX123 has also performed as an optimal catalyst for:
- Buchwald-Hartwig amination of arylamines with (hetero)aryl bromides
- intramolecular Buchwald–Hartwig coupling of an N-protected secondary amine with an aryl bromide
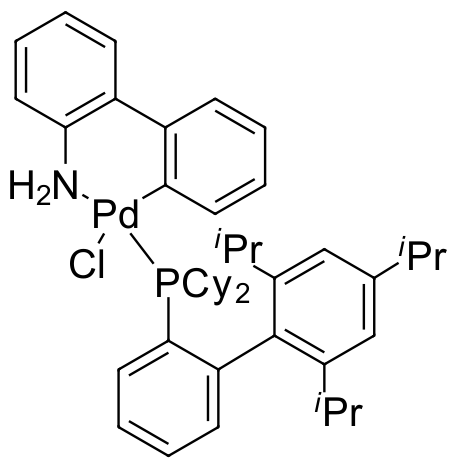
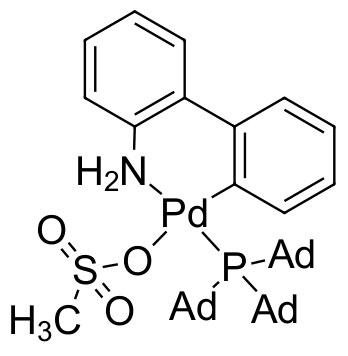
Umicore CX132 - Pd(XPhos)G3
CAS Number: 1445085-55-1
Empirical formula: Pd(XPhos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)](Ms)
CX132, also known as Pd(XPhos)G3, is a broadly utilized, air- and moisture-stable, 3rd generation Buchwald catalyst which is considered “a ‘commodity’ in many medicinal chemistry laboratories.” [[email protected]]
CX132 has been an effective catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura couplings of unstable boronic acids with aryl chlorides, boronic esters with aryl bromides, and meta-phosphonate substituted aryl boronic acids with aryl bromides. Another significant use of CX132 has been Negishi couplings of heteroaryl zinc reagents and heteroaryl chlorides, bromides and triflates.
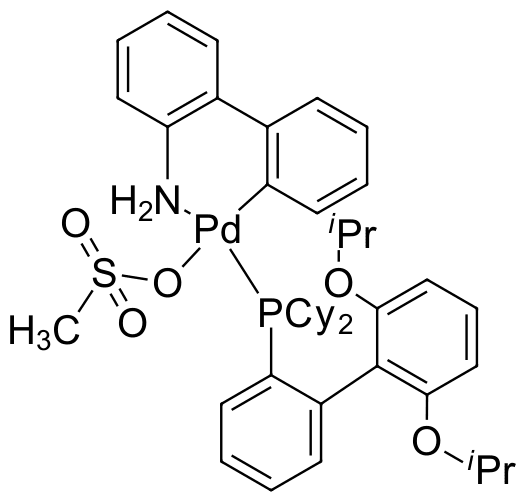
Umicore CX133 - Pd(RuPhos)G3
CAS Number: 1445085-77-7
Empirical formula: Pd(RuPhos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)](Ms)
CX133, also known as Pd(RuPhos)G3, is a third generation Buchwald precatalyst and has been demonstrated to be highly efficient at catalyzing Buchwald-Hartwig couplings of (hetero)aryl chlorides with secondary amines. It has also been utilized as a premier catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura polymerizations where rapid catalyst activation and turnover prohibit deleterious side reactions. CX133 has also found utility for the Suzuki coupling of a heteroaryl tosylates and aryl boronic acids, intramolecular amination to form indoles, perfluoroalkylative aryloxycarbonylation of alkynese, Pd-catalyzed Hofman eliminationf , and Pd/Cu catalyzed arylboration.
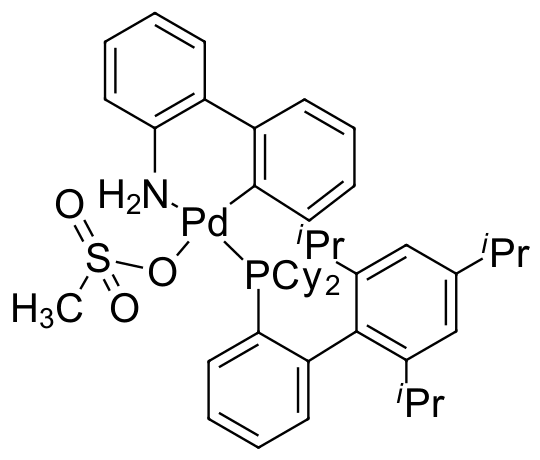
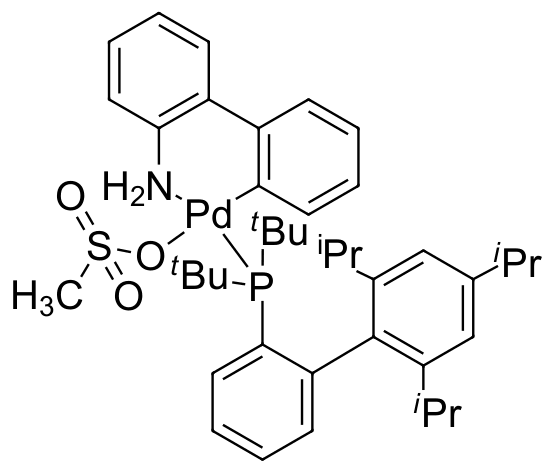
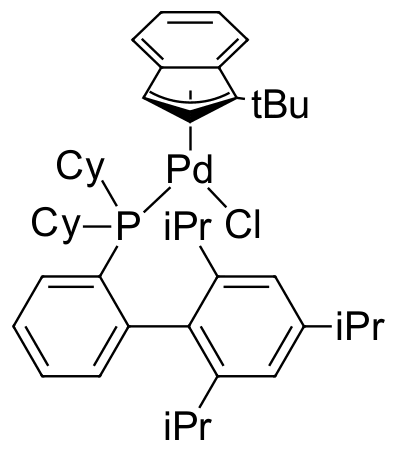
Umicore CX135 - Pd(tBuXPhos)G3
CAS Number: 1447963-75-8
Empirical formula: Pd(tBuXPhos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)](Ms)
CX135, also known as Pd(tBuXphos)G3, is a third generation Buchwald cyclometallated precatalyst. CX135 has been demonstrated to be an extremely effective catalyst for C-N bond formation (amination and amidation):
- amination of a polysubstituted 2-pyridine and 2-amino-5-hydroxypyridine
- amination of iodo quinoline-2-one derivatives with glucosamine
- amination of 3-halopyridine with secondary amines
- amination of methyl 6-bromonicotinate with 2,2,2-trifluoroethan-1-amine
- amination of 2-halopyridine with 2-amino-6-methylpyridine
- N-arylation of aminosugar
- heteroaryl amidation
- amidation of aryl nonaflates
Additional transformation where CX135 has excelled include:
- cyanation of (hetero)aryl halides and triflatesi where ligand sterics have been hypothesize to aid
in protecting the Pd - center from poisoning as a result of ligand exchange with cyanide.
- defluorinative Coupling of gem-difluoroalkenes and acyl chlorides
- Cu/Pd-catalyzed cis-borylfluoroallylation of alkynes
- para-C- H Arylation of sterically N-protected anilines with aromatic halides
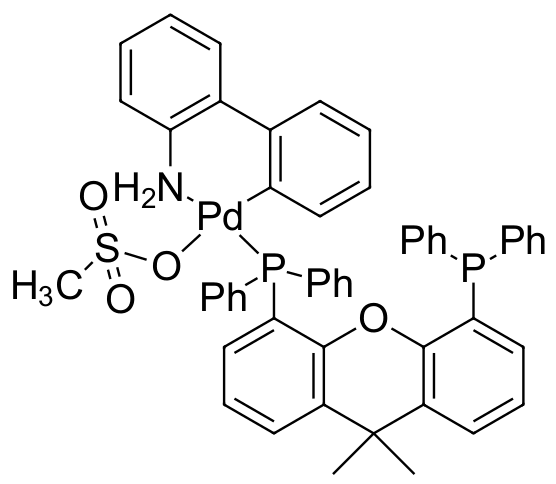
Umicore CX136 - Pd(Xantphos)G3
CAS Number: 1445085-97-1
Empirical formula: Pd(Xantphos)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)](Ms)
CX136, also known as Pd(Xantphos)G3, has been particularly effective for the formation of C-S bonds:
- preparation of biaryl sulfoxides via C-S bond formation
- iodoquinoline thiolation
- C–S bond formation between 1-thiosugars and bromobenzothiadiazol
- multi component coupling of thiosugars, boronic acid, and iodo-bromoarenes
- coupling of thiosugars with iodoglycals
- coupling of thiosugars or protected cysteine with aryl iodides
- synthesis of macrocyclic peptides by palladium-catalyzed multiple S‑arylation
- preparation of aryl vinyl sulfides via the reaction of aryl bromides and 1,3-oxathiolanes
CX136 has also demonstrated the ability to be highly efficient for C-C bond formations:
- enantioselective synthesis of α-alkylated pyrrolesi and aryl acetic acid estersj via
cooperative isothiourea/Pd catalysis - preparation of 4-alkylated isocoumarins via Pd-Catalyzed α‑Arylation of ketones or aldehydes with aryl bromides
- α-Arylation of protected S,S-Dimethylsulfoximine with (hetero)aryl bromides
- mono-g-arylation of 7-methoxy-4-methylcoumarin with aryl halides and triflates
- multi component alkyl carbamoylation/cyanation of alkenes induced by visible light
- Heck reactions with tertiary alkyl halides or functionalized alkyl halides
- branch-selective acyclic sec-alkyl Negishi cross-couplings with heteroaryl halides
- Suzuki coupling of an enol triflate and aryl boronic acid
- cyanation of (hetero)aryl halides
Lastly, C136 has been the optimal catalyst for select C-N couplings and an unusual C-Se bond formation:
- amidation of bromonaphthalimides
- three component aminocarbonylation of aryl bromides
- coupling of selenoglycosides with (hetero)aryl or alkenyl halides
Catalysts applying Buchwald ligands or Buchwald palladacycles involving other ligands:
Umicore CX221
CAS Number: 1779569-07-1
Empirical formula: Pd(SPhos)(1-tBu-Ind)Cl
CX221, also known as Pd(SPhos)(1-tBu-Ind)Cl, is a new cyclometallated catalyst featuring SPhos and the highly reactive h3-1-tBu(indenyl) moiety. Is has been optimally applied to the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of unprotected indazoles or benzimidazolesa where typical reactions were conducted in the mixed solvent system Dioxane/MeOH utilizing K2CO3 as a base at 80 °C.
Reference: a. 10.1021/acscatal.5b00878
Umicore CX222
CAS Number: 1779569-07-1
Empirical formula: Pd(SPhos)(1-tBu-Ind)Cl
CX222, also known as Pd(XPhos)(1-tBu-Ind)Cl, is a new cyclometallated catalyst featuring XPhos and the highly reactive h3-1-tBu(indenyl) moiety. Suzuki-Miyaura couplings of heterocyclica or aromaticb boronic acids with aryl chlorides in mixed solvent systems (THF/MeOHa or THF/H2Ob) with potassium bases (K2CO3a or K₃PO₄b) at ambientb or slightly elevateda (40 °C) temperatures.
References:
a. 10.1021/acscatal.5b00878
b. 10.1002/adsc.202000987
Umicore CX401 - Pd(PAd3)G3
CAS Number: 2252175-57-6
Empirical formula: [Pd(PAd3)[2-(2'-amino-1,1'-biphenyl)](Ms)]
CX401, also known as Pd(PAd3)G3, is a unique third generation Buchwald precatalyst featuring the extremely bulky, and highly electron donating tris(adamantly)phosphine. CX401 has demonstrated unparallelled reactivity for the stereoinvertive Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of enantioenriched alkylboron nucleophiles with aryl chloridesa. Reactions proceeded in the mixed solvent system of toluene/H2O at moderate temperature (60 °C), with K2CO3 as base.
Reference: a. 10.1126/science.aat2299
Umicore CX737
CAS Number: 3053769-87-9
Empirical formula: Pd(α-MeNAP)(tBuBrettPhos)Br
CX737, systematically known as Pd(α-MeNAP)(tBuBrettPhos)Br, is a structurally unique, bench-stable complex representing a significant advance in one-component catalyst design for selective cross-coupling reactions. While reversible insertion of the aryl ring of the ligand into the Pd-MeNAP bond generates a novel precatalyst architecture, activation cleanly affords the traditional LPd0 complex. Despite its recent inception, CX737 has been documented to be highly efficient and selective for the monoarylation of ammonia and hydrazine. Notably, it was shown to outperform in situ combinations of tBuBrettPhos with a variety of palladium precursors, including CX700. Given this remarkable activity, it is anticipated that CX737 will find utility in other challenging C-N and C-C bond forming reactions.
Reference: 10.1021/acscatal.4c02624