YPhos ligands for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions
Highly electron-rich ylide substituted phosphines enabling unprecedented efficiency and versatility
When combined with a suitable palladium precursor, the YPhos family of ligands offers several significant advantages:
- Facile coupling of aryl halides, particularly aryl chlorides, which are typically challenging substrates for cross-coupling reactions1-4.
- Mild reaction conditions are appropriate, which can result in improved selectivity as fewer side reactions are observed.
High activity in C-N and C-C cross-coupling reactions1-8. - It allows for the coupling of organolithium, magnesium, and zinc reagents, broadening the range of possible reactions and substrates that can be used5,6,8.
These advantages make YPhos ligands particularly useful for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, Additionally, they are suitable for a variety of applications, including the Buchwald-Hartwig amination and a-arylation of aliphatic cyclic ketones1-4,7.
Key Features & Characteristics
YPhos cross-coupling technology is distinguished by several key features and characteristics that contribute to its effectiveness and sustainability in chemical synthesis:
Key Features10
- Unique Bonding Motif: The ligands bind to the metal through both the phosphine and ylidic carbon site, leading to a unique and stable bonding arrangement.
- Simplicity and Efficiency: Despite their simple structure, YPhos–PdCl2 complexes are highly efficient precatalysts for a variety of coupling reactions.
- Reduced Catalyst Loading: The high efficiency of YPhos allows for lower amounts of catalyst to be used, which is cost-effective and reduces waste.
Contribution to Sustainable Chemistry
- Milder Reaction Conditions: YPhos catalysts enable reactions to proceed under milder conditions, which can reduce energy consumption and minimize the generation of hazardous byproducts.
- Versatility: The ability to efficiently couple a wide range of substrates reduces the need for multiple specialized catalysts, streamlining the synthesis process and reducing chemical waste.
- Improved Large-Scale Processes: The use of YPhos specifically, and catalysis generally in large-scale processes demonstrates an improvement in the sustainability of industrial chemical production.
These characteristics make YPhos catalysts an important tool in the evolution of sustainable chemistry, offering a more efficient and eco-friendly approach to chemical synthesis.
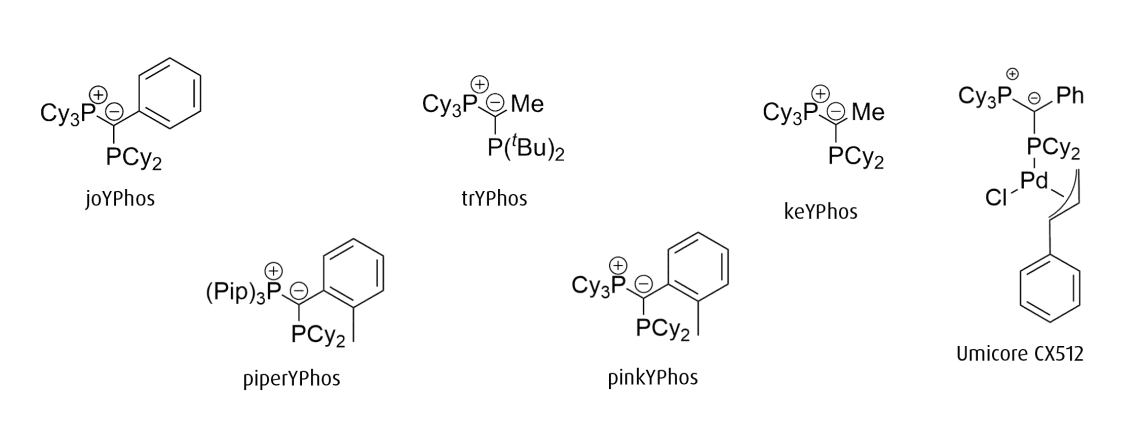
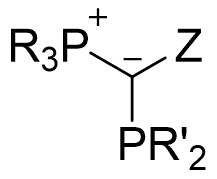
While ylide-functionalized phosphines are generally highly electron-rich, three key points of variation allow for tuning the precise electronic and steric environment they impart on the metal center. They are:
1. R’ on the coordinating phosphine (PR’2)
2. R on the phosphonium moiety (PR3)
3. the backbone substituent (Z)
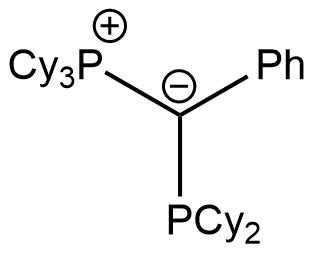
joYPhos
Tricyclohexyl((dicyclohexylphosphanyl)(phenyl)methylene)phosphane
CAS Number: 2271302-85-1
Chemical formula: C37H60P2
Empirical formula: PCy3C(Ph)PCy2
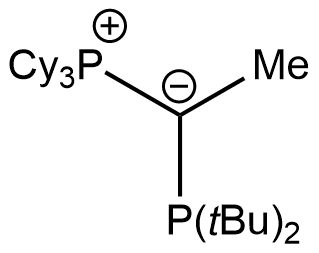
trYPhos
Tricyclohexyl(1-(di-tert-butylphosphanyl)ethylidene)phosphane
CAS Number: 2271302-83-9
Chemical formula: C28H54P2
Empirical formula: PCy3C(Me)PtBu2
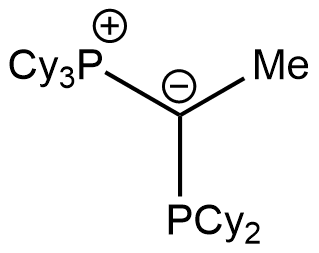
keYPhos
Tricyclohexyl(1-(dicyclohexylphosphanyl)ethylidene)phosphane
CAS Number: 14185-94-5
Chemical formula: C32H58P2
Empirical formula: PCy3C(Me)PCy2
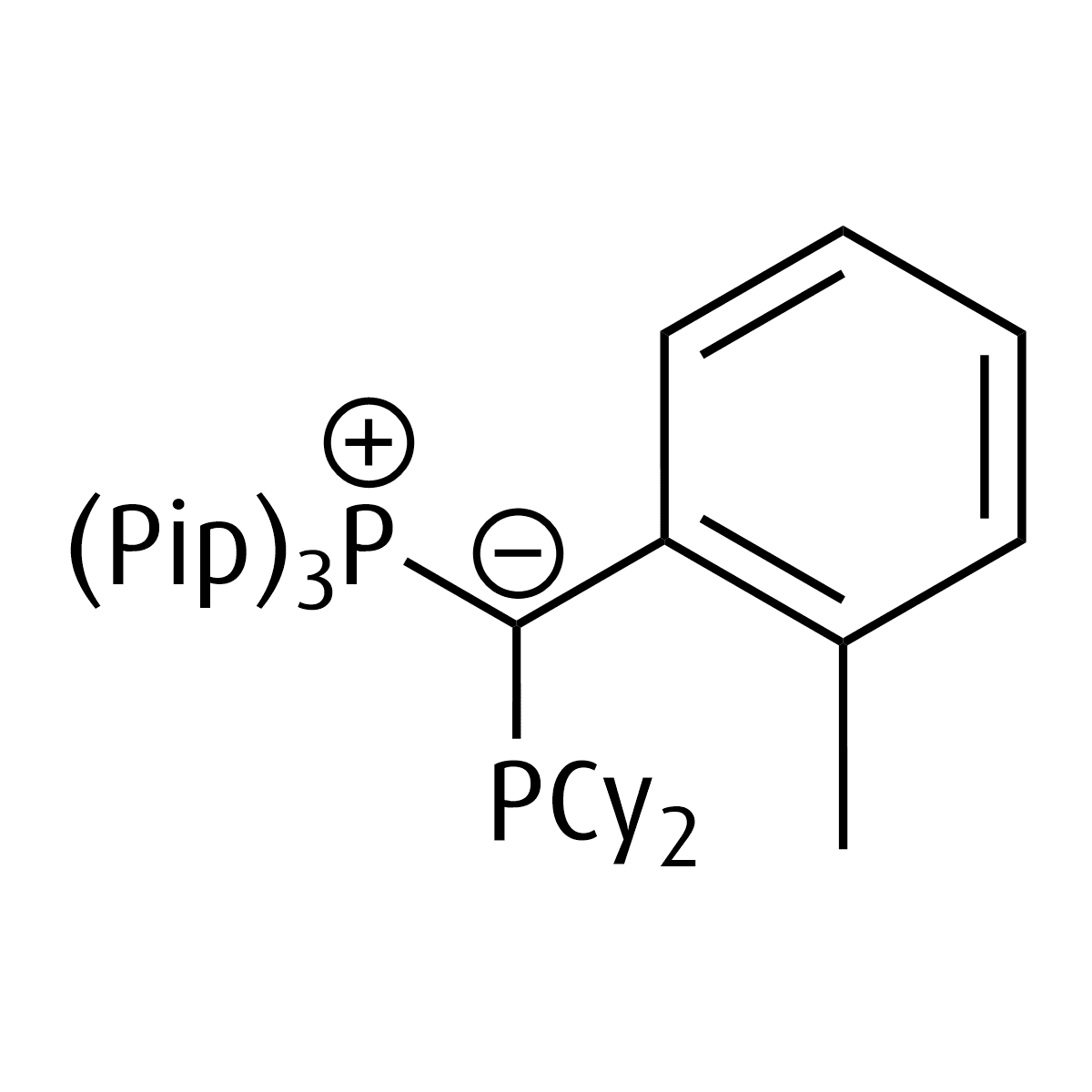
piperYPhos
Tris(1-piperidyl)((dicyclohexylphosphanyl)(2-tolyl)methylene)phosphane
Chemical formula: C35H59N3P2
Empirical formula: PPip3C(o-Tol)PCy2
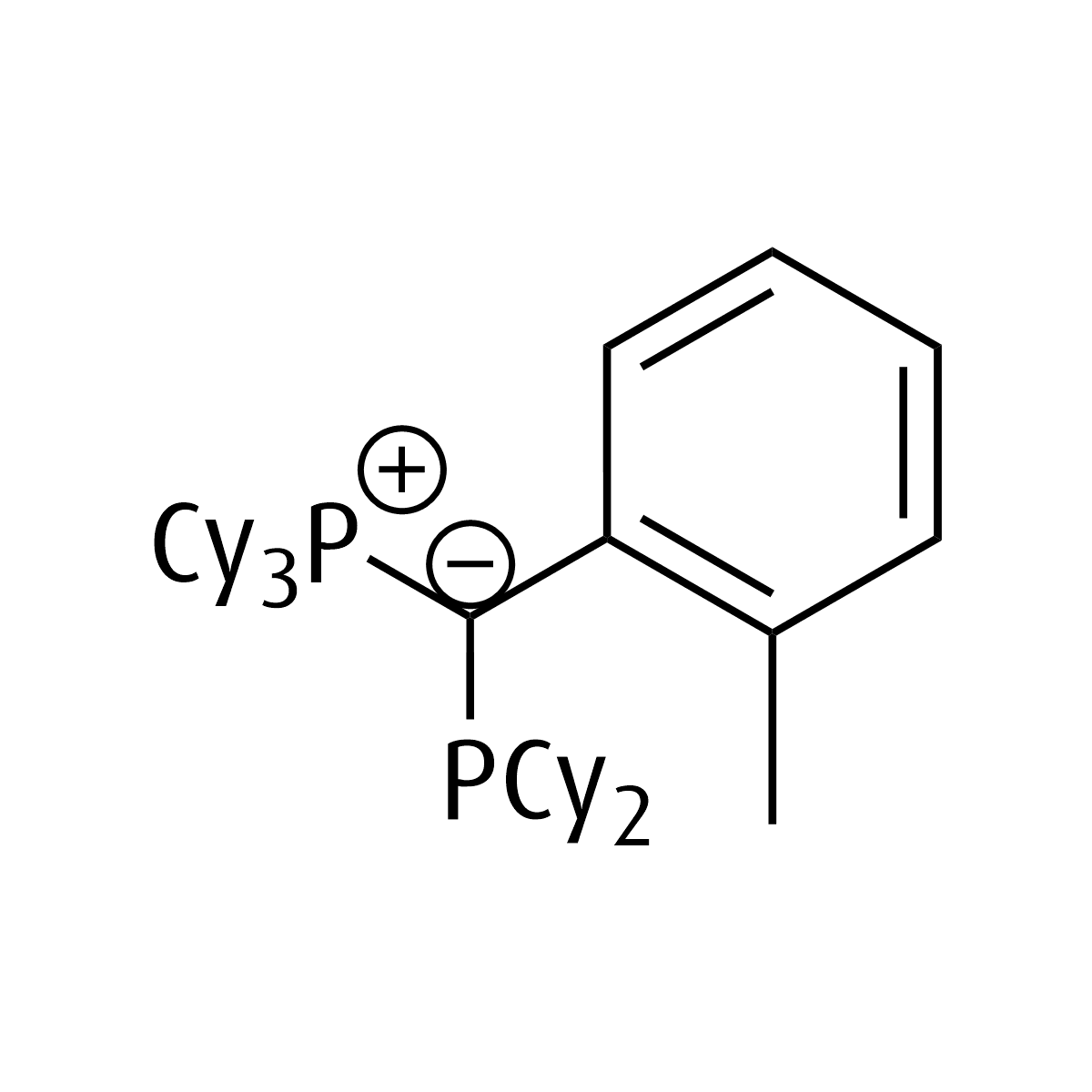
pinkYPHos
Tricyclohexyl((dicyclohexylphosphanyl)(2-tolyl)methylene)phosphane
CAS Number: 2495200-15-0
CAS Number 2: 2495200-11-6
Chemical formula: C38H62P2
Empirical formula: PCy3C(o-Tol)PCy2
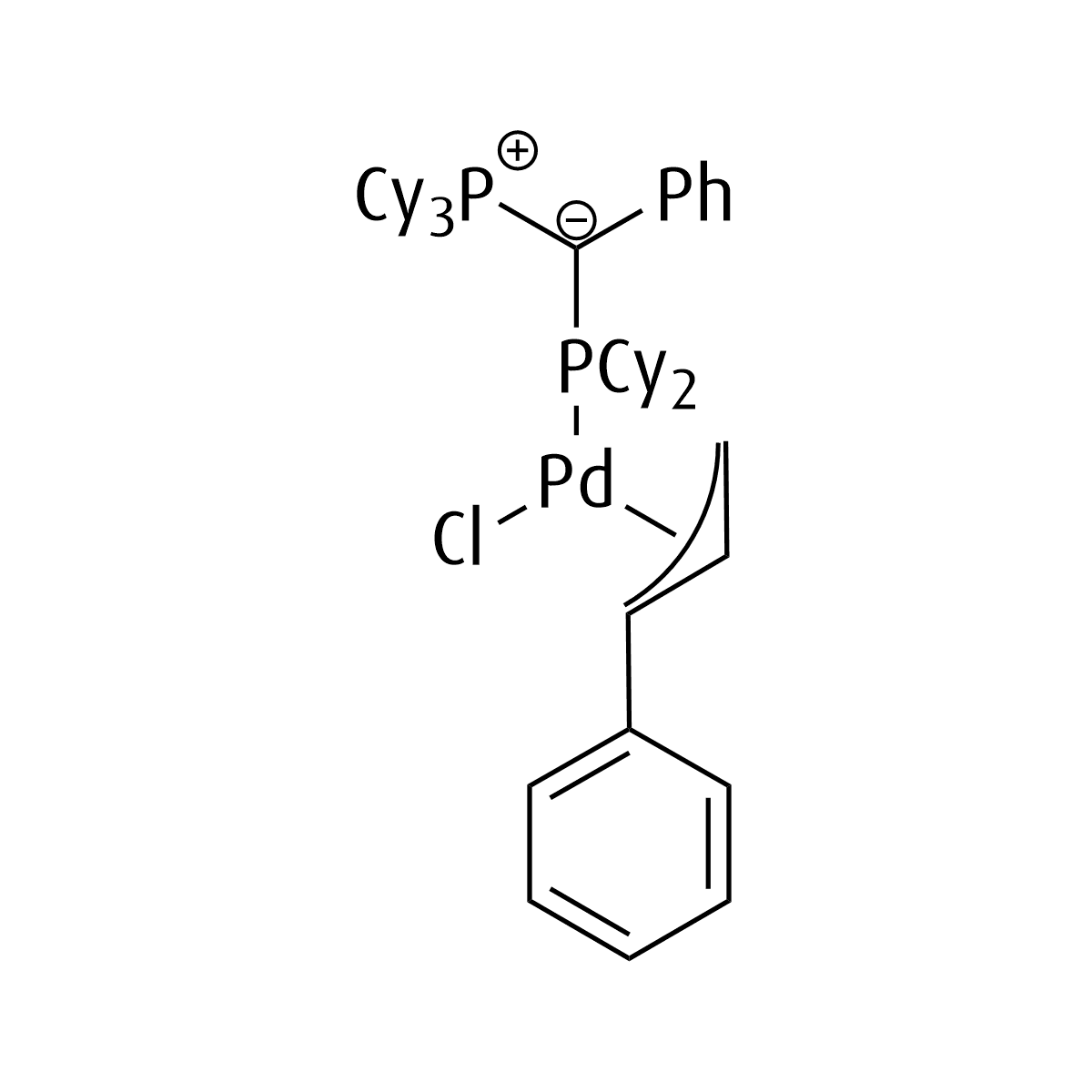
Umicore CX512
Chlorophenylallyl(tricyclohexyl((dicyclohexylphosphanyl)(phenyl)methylene)phosphine)palladium(II)
CAS Number: 2412537-46-1
Chemical formula: C46H69ClP2Pd
Empirical formula: Pd(joYPhos)(cinnamyl)Cl
The Technology
Imagine YPhos as a master key in the world of chemistry. It’s a specialized compound that acts like a facilitator for certain chemical reactions, specifically those that join two different molecules together. This process is akin to connecting Lego blocks, where YPhos helps to snap them together with ease and precision. Its role is crucial in creating complex molecules, which can be used in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and more. The beauty of YPhos lies in its ability to perform these connections under conditions that are less harsh, making it a go-to choice for chemists looking to build molecules in a more efficient and cleaner way.
Ylide-functionalized phosphines are a recent addition to the field of highly electron-rich ligands for palladium-based couplings. Their direct and modular synthesis permits a broad variety of steric and electronic parameters. This flexibility has enabled their application in several catalytic transformations such as the Buchwald-Hartwig amination of aryl chlorides1-4, the alkylation of aryl chlorides with lithium5, magnesium8, or zinc reagents6, and the monoarylation of alkyl ketones with aryl chlorides7.
Benefits & Applications
Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions have found a home in a variety of industries. The need to efficiently and reliably construct carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds is shared by chemists in numerous industries: pharmaceuticals, materials science, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. In recognition of the impact of these methodologies, pioneering work by Richard F. Heck, Akira Suzuki, and Ei-ichi Negishi were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
YPhos ligand technology is a game-changer in the field of palladium-catalyzed bond-formations, offering a plethora of benefits and applications across various industries. Below are some of the key advantages and applications:
- High Efficiency: YPhos catalysts are known for their exceptional activity in coupling reactions, making them highly efficient for industrial-scale processes.
- Stability: Free ligands and resulting catalysts display reasonable stability though handling under inert conditions and utilizing air and moisture free solvents is recommended.
- Versatility: The ability to couple a wide range of substrates, including challenging aryl chlorides, makes YPhos catalysts versatile tools in synthesis.
- Mild Conditions: Reactions with YPhos can often be conducted under milder conditions, which is beneficial for selectivity and the stability of sensitive molecules.
- Pharmaceuticals: In drug development, YPhos catalysts are employed for creating complex molecules, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), through efficient C-C and C-N bond formation.
- Materials Science: These catalysts are used to synthesize advanced materials, including organic electronics and polymers, by facilitating the formation of intricate molecular architectures9.
- Agrochemicals: YPhos technology plays a role in producing agrochemical compounds, where precise and efficient synthesis is crucial for developing safe and effective products.
- Fine Chemicals: The catalysts are instrumental in the production of fine chemicals, where high purity and quality are required.
- Buchwald-Hartwig Amination: A cornerstone transformation in pharmaceutical synthesis; YPhos complexes have shown exceptionally high activities in these aminations1-4.
- Murahashi-Feringa Coupling: YPhos complexes enhance the efficiency of alkyl lithium cross-coupling reactions with aryl halides, allowing for the facile formation of carbon-carbon bonds5.
Success Stories
Expanding the scope of traditional Palladium-catalyzed transformations to aryl chlorides:
- amination of aryl chlorides1-4
- alkylation of aryl chlorides with lithium reagents5
- alkylation of aryl chlorides with Reformatsky reagents6
- monoarylation of alkyl ketones with aryl chlorides7
Frustrated Lewis Pair catalyzed polymerization9
1. Weber, P.; Scherpf, T.; Rodstein, I.; Lichte, D.; Scharf, L. T.; Gooßen, L. J.; Gessner, V. H. A highly active Ylide‐Functionalized phosphine for Palladium‐Catalyzed aminations of aryl chlorides. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2019, 58 (10), 3203–3207. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201810696.
2. Tappen, J.; Rodstein, I.; McGuire, K.; Großjohann, A.; Löffler, J.; Scherpf, T.; Gessner, V. H. Palladium Complexes based on Ylide‐Functionalized Phosphines (YPHOS): broadly applicable High‐Performance precatalysts for the amination of aryl halides at room temperature. Chemistry - a European Journal 2020, 26 (19), 4281–4288. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201905535.
3. Rodstein, I.; Prendes, D. S.; Wickert, L.; Paaßen, M.; Gessner, V. H. Selective Pd-Catalyzed Monoarylation of Small Primary Alkyl Amines through Backbone-Modification in Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines (YPhos). The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85 (22), 14674–14683. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.0c01771.
4. Neigenfind, P.; Knyszek, D.; Handelmann, J.; Gessner, V. H. Synthesis of sterically encumbered di- and triarylamines by palladium-catalysed C–N coupling reactions under mild reaction conditions. Catalysis Science & Technology 2022, 12 (11), 3447–3453. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cy02352g.
5. Scherpf, T.; Steinert, H.; Großjohann, A.; Dilchert, K.; Tappen, J.; Rodstein, I.; Gessner, V. H. Efficient Pd‐Catalyzed Direct Coupling of Aryl Chlorides with Alkyllithium Reagents. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59 (46), 20596–20603. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202008866.
6. Hu, Z.; Wei, X.; Handelmann, J.; Seitz, A.; Rodstein, I.; Gessner, V. H.; Gooßen, L. J. Coupling of Reformatsky Reagents with Aryl Chlorides Enabled by Ylide‐Functionalized Phosphine Ligands. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, 60 (12), 6778–6783. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202016048.
7. Hu, X.-Q.; Lichte, D.; Rodstein, I.; Weber, P.; Seitz, A.-K.; Scherpf, T.; Gessner, V. H.; Gooßen, L. J. Ylide-Functionalized Phosphine (YPhos)–Palladium Catalysts: Selective Monoarylation of Alkyl Ketones with Aryl Chlorides. Organic Letters 2019, 21 (18), 7558–7562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02830.
8. Daeschlein-Gessner, V.; Rodstein, I.; Scherpf, T.; Doppiu, A. ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDS, PRODUCTION AND USE THEREOF. WO2023198596A1, October 19, 2023.
9. Su, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X. Rare-Earth Aryloxide/Ylide-Functionalized phosphine frustrated Lewis pairs for the polymerization of 4-Vinylpyridine and its derivatives. Macromolecules 2021, 54 (17), 7724–7731. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.1c01339.
10. Rodstein, I.; Kelling, L.; Löffler, J.; Scherpf, T.; Sarbajna, A.; Andrada, D. M.; Gessner, V. H. Formation of exceptional monomeric YPhos–PdCl2 complexes with high activities in coupling reactions. Chemical Science 2022, 13 (45), 13552–13562. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sc04523k.
Daniel Knyszek, Julian Löffler, David E. Anderson, Eva Hevia, and Viktoria H. Gessner
Harnessing Organopotassium Reagents for Cross-Coupling with YPhos-Pd Catalysts: Opportunities, Applications, and Challenges;
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2025 147 (6), 5417-5425
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c18073?utm_source=SendGrid_ealert&utm_medium=ealert&utm_campaign=TOC_jacsat_v147_i6
J. Löffler, N. Kaiser, D. Knyszek, K.-S. Feichtner, M. Jörges, F. Krischer, V. H. Gessner*
P,N-coordinating Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines (NYPhos): A Ligand Platform for the selective Monoarylation of small Nucleophiles
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202408947. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202408947
D. Knyszek, V. H. Gessner*
Ylide-Substituted Phosphines in Palladium-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions
Aldrichimica Acta 2024, 57, 17 – 28.
S. Manna, F. Papp, Y. Hisata, J. Löffler, M. Rybka, V. H. Gessner,* Y. Hoshimoto,* L. J. Goossen*
Palladium-Catalyzed γ-Arylation of Acylketene Synthons with Aryl Chlorides Enabled by Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines (YPhos) Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.202301474.
A. Burhenn, R. Bavaro, V.H. Gessner
Pd-catalysed hydrodehalogenation of aryl chlorides: a mild method for deuteration and detoxification
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2023, 13, 3545-3550. doi: 10.1039/D3CY00432E
I. Rodstein, A. Doppiu, V.H. Gessner*
Ylide-Functionalized Phosphine (YPhos) Platinum Complexes: Synthesis and Application in Hydrosilylations at Mild Conditions
Organometallics 2023, 42, 1021-1029. doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.3c00156
F. Papp, D. Sowa Prendes, S. Manna, A-K. Seitz, S. Kostiukovska, J. Löffler, V.H. Gessner*, L.J. Gooßen*
Palladium-Catalyzed Arylation of Hydantoins with Aryl Chlorides Enabled by Ylide-Functionalized Phosphines (YPhos)
ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6846-6850. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c01403
J. Löffler, S.M.P. Vanden Broeck, C.S.J. Cazin, S.P. Nolan, V.H. Gessner
Correlation of Experimental and Calculated Reaction Enthalpies with Ligand Donor Strengths
Chem. Eur. J. 2023, e202300151. doi: 10.1002/chem.202300151
I. Rodstein, V.H. Gessner*
Carbanion-functionalized phosphines: New design elements for catalyst development
Adv. Catal. 2023, 72, 1-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acat.2023.07.002
J.F. Goebel, J. Löffler, Z. Zeng, J. Handelmann, A. Hermann, I. Rodstein, T. Gensch, V.H. Gessner, L.J. Gooßen
Computer-Driven Development of Ylide Functionalized Phosphinesfor Palladium-Catalyzed Hiyama Couplings
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202216160. doi: 10.1002/anie.202216160
X.-J. Wei, B. Xue, J. Handelmann, Z. Hu, H. Darmandeh, V.H. Gessner*, L.J. Gooßen*
Ylide-Functionalized Diisopropyl Phosphine (prYPhos): A Ligand for Selective Suzuki-Miyaura Couplings of Aryl Chlorides
Adv. Synth.Catal.2022, 364, 3336-3341. doi: 10.1002/adsc.202200321
S. Lapointe, A. Sarbajna, and V.H. Gessner*
Ylide-Substituted Phosphines: A Platform of Strong Donor Ligands for Gold Catalysis and Palladium-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 5, 770–782. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00797